Studies show that the healthcare industry spends about $2.1 billion each year on error-prone and poorly performed manual tasks around data management. This problem became more evident with the COVID-19 pandemic as there was an exponential increase in the number of people seeking medical attention.
To reduce operational costs, prevent human error in processing data, and increase operational efficiency, more and more hospitals are implementing robotic process automation (RPA) systems. Research done by Gartner concludes that 50 percent of US healthcare providers will invest in RPA by 2023.
This article will discuss the benefits of RPA in the healthcare industry, how RPA systems work, use cases and real-life examples of RPA in healthcare, and how to approach automation.
RPA in healthcare
Robotic process automation refers to a technology mimicking repetitive human interactions with software applications. It delegates routine tasks to bots, saving employees time for higher-value work and boosting the accuracy of the basic procedures.
All RPA bots fall into two large groups — attended and unattended. Attended RPA resides on the desktop, acting as a personal assistant to employees. The bots must be manually triggered to perform their tasks. Among other things, they can
- copy and paste data,
- share clinical information,
- validate data against legal protocols,
- fill in standard medical forms, and
- generate reports.
With unattended bots, no human involvement is necessary. Instead, they follow predefined rules and schedules to start or stop operating in the background. Such RPA can be configured to
- open emails and attachments and download them to the computer;
- connect and log in to apps via APIs;
- extract data from medical documents; and
- perform other back-office operations.
More often than not, both types of automation are involved in the hospital workflow to support process continuity. For example, if a back-office RPA fails to complete an operation, it triggers a front desk agent that, in turn, will alert a human employee to review the task and resolve the problem. Working as a team, bots can bring medical companies the following benefits.
Cost reduction. According to a study conducted by CAQH, healthcare organizations can save up to $13.3 billion if they automate administrative tasks.
Decreased rate of missed appointments. With the help of RPA bots that schedule and send reminders, people are less likely to miss their appointments with the doctors.
Elimination of human error. Robots are better at following rules and less likely to make mistakes than human employees. Implementing RPA systems decreases the number of errors that cause the organization to lose money.
Better patient experience. RPA systems process patient requests quicker, thereby decreasing the time people need to wait for responses.
Increased employee satisfaction. Since RPA systems eliminate repetitive, time-consuming, and tedious administrative tasks, employees can concentrate on providing quality care to patients.
To understand how all these advantages can be delivered, let's talk about the technologies behind robotic process automation.
Technologies behind RPA solutions
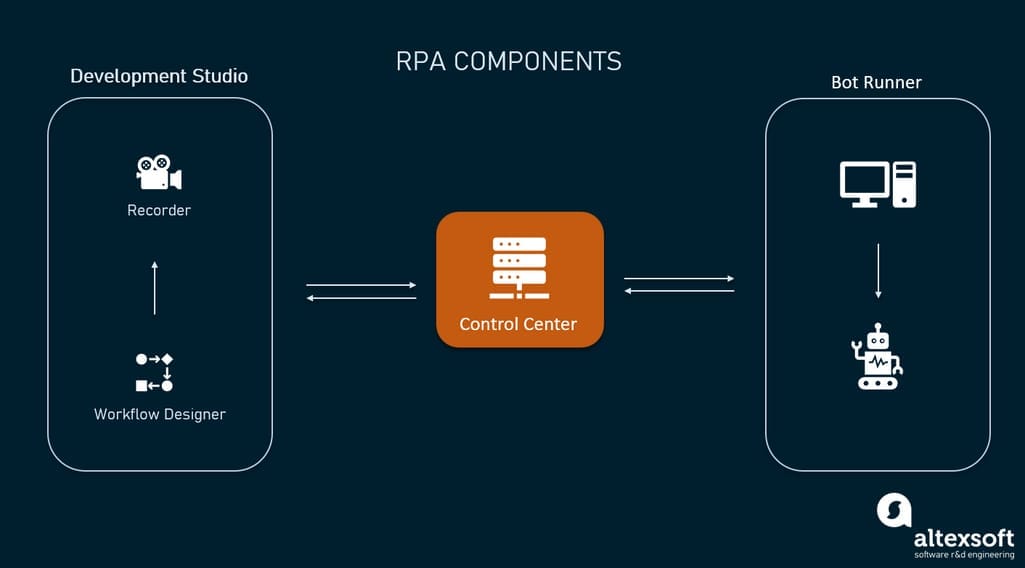
Healthcare or not, the most straightforward way to implement bots into daily workflow is via a ready-to-use RPA system. While RPA systems can somewhat differ from vendor to vendor, their most common components are:
- a development environment to design, test, and debug bots;
- a control center to schedule and manage bots; and
- a bot runner to execute the scripts on the production environment.
RPA tool components
The Development Environment — often called the Development Studio — is a workspace to design workflows, write RPA scripts, and define triggers for executing them. It’s worth noting that many modern systems don’t require knowledge of programming languages. Instead, you can use intuitive drag-and-drop tools.
The critical component of the Development Studio is a recorder. It allows creating an automation sequence by having the bot record an employee’s actions, such as hovering, scrolling, and copying information. When the recording is stopped, the operations and actions are converted into instructions for automated, programmatic repetitions of that sequence.
Control Center is a dashboard for scheduling and managing bots and scaling their activities. It executes the bots created in the development environment on the bot runner. The bots also report the execution status (pass, fail, execution logs, etc.) to the control center.
Bot Runners execute bots on a schedule set up in the Control Center. In the case of an attended RPA, the script will be triggered by a human.
Advanced systems can go beyond the traditional functionality by augmenting RPA with AI and giving bots decision-making and cognitive capabilities. While common bots can only perform simple operations they are instructed to do, they are independent and can cope with some complex tasks.
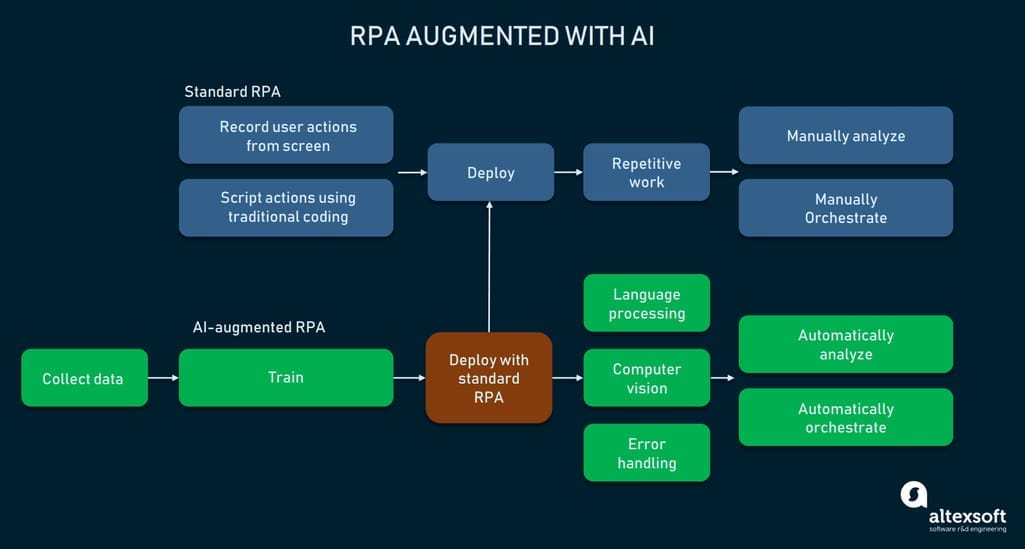
Standard RPA implementation can be augmented with additional AI-driven capabilities.
One of the most popular applications of AI-powered RPA systems in healthcare is intelligent document processing. It involves such technologies as
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to recognize fragments of text within scanned documents and “translate” them into digital format;
- computer vision to classify documents; and
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) to extract meaningful data elements (like email, phone numbers, names, and other protected health information) from texts.
Now, let’s see how it works in real life.
Use cases and real-life implementation of RPA in healthcare
RPA has been heavily adopted in sectors such as banking, retail, and human resources. The healthcare industry is gradually upping its game, with bots now taking part in key procedures.
Payment processing
Payment processing involves handling numerous invoices that contain patient costs like test fees, doctor’s consultation fees, and ward costing. The software robots can automatically collect, match, standardize, and transform benefit and eligibility data from insurers and combine all of it with contracted rates and charges to estimate a patient’s cost. For example, if a patient needs an appendectomy, the standard RPA bots log into his insurer’s website to collect information on wether that operation is covered or not. This information is then combined with data on previous costs for similar operations to estimate how much the patient will pay. The AI-based RPA assistants then use ML algorithms determine the cost based on previous insurance claims and estimates the cost. The model is regularly updated with new data to constantly improve its accuracy. Since the estimates are provided in advance, fewer patients cancel their appointments.
A good example of using RPA for payment processing is Baylor Scott & White Health (BSWH), an academic medical organization encompassing 52 hospitals in Texas. For more than eight years, it had been looking for a solution capable of improving patient financial experience, reducing the cost of collecting invoices, and optimizing its net revenue. Finally, they achieved all of this by implementing AI-fueled RPA tools from Waystar.
The technology estimates patient care costs prior to providing treatment. Previously, the calculations were made manually, took an employee about 5 - 7 minutes, and had low accuracy. Now, thanks to the AI and RPA, 70 percent of estimates are produced without human involvement, and the process generally takes less time and results in fewer errors. Also, BSWH saw a 60 - 100 percent improvement in point-of-service collections.
Insurance claims processing
When done manually, claims processing is time-consuming and, what's worse, highly prone to error. According to AARP, 200 million claims are rejected every year for various reasons. One of the most prominent reasons for denial is paperwork error.
How can automation help in this case? Let’s again take a look at BSWH that also uses the RPA solution for claim processing in their insurance collections sector.
Prior to using RPA, collectors needed to log into various payer accounts or call them manually. Now, the bot automatically signs into payer websites to check the status of outstanding claims. Once the claim is accepted, it is scheduled for payment. This streamlines the workflow of collectors. As a result, they interact only with claims that have been denied and need reviewing. Also, the AI-powered technology predicts the propensity of an insurance claim denial or payment.
Medical document processing
Healthcare providers have a near-impossible task to ensure the best patient care while keeping up with administrative tasks. Battling with lots of documentation, both paper and electronic, doctors and nurses are required to process them as fast as possible, all while tending to patients.
RPA tools can solve this problem through built-in models that use integrated rules and machine learning algorithms. The robots learn from recorded data of clicks and actions on the screen and classify medical documents into different categories like insurance cards, claims forms, medical reports, etc. It can also extract, interpret, and process data from PDFs, handwriting, emails, images, and scans.
For example, the US Food And Drug Administration (FDA) has to process a mountains of electronic health files daily with speed and accuracy. For this, the organization responsible for public health turned to ABBYY’S Digital Intelligence platform that can capture and collect important data from medical reports. This tool ensures that the necessary details extracted from the complex documents have more than 99 percent accuracy.
Appointment scheduling
Patient appointment scheduling is a tedious process involving collecting data, diagnosis, insurance details, social security, and lots of other information. Patients need to also ensure that their availabity coincides with the doctor’s, which can be difficult to do. RPA tools can solve these problems by automating the data collection process and matching the patients with doctors based on availability, diagnosis, location, standards, and more. These RPA tools can send the patients regular reminders not to miss their appointments. It also alerts the patients in case the doctor is unavailable and modifies or makes new appointments. A good example is the UIPath appointment manager for clinics.
UiPath partnered with Swiftqueue to create a cloud-based scheduling platform for hospitals used by healthcare organizations in the UK, US, Ireland, and Canada. This tool helps to schedule patients for doctor appointments and lab tests.
The software bots get into hospital records systems, collect patient data and doctor availability slots in all departments, and send them to the scheduling platform. Now, the patients have access to personal accounts with all appointment details. From their accounts, they can cancel or reschedule appointments. This solution can save costs in many countries where appointments are made by post and can only be rescheduled on the phone.
How to approach RPA
The RPA implementation encompasses several key stages for employing bots and making them work.
Process mining. First, you must access all the operations within and across various departments of the healthcare organization. This is called process mining. This aims to figure out which processes can be automated to save time and resources—for example, appointment scheduling, document processing, and claims processing.
Find an RPA developer. As we mentioned above, most platforms support drag-and-drop tools to build bots with no code. However, for designing more complex workflows, you will need an RPA developer. These specialists not only build, test, and maintain bots but also help companies at earlier stages. They participate in gathering requirements, creating technical documentation, and choosing an RPA platform.
Choose the right platform. You should choose your RPA solution based on the tasks that the healthcare organization wants to automate. Some tasks may need cognitive automation, which involves technologies like Natural Language Processing (patient scheduling) or computer vision (document processing).
Devise a structured plan. Your plan should go beyond implementation and consider other factors like process scalability, financial stability, and future-readiness. With unattended RPA, you may need a larger investment, while attended RPA may require a smaller system. Irrespective of the type of automation, you need to test it with a few tasks and, if successful, scale the RPA tool to take on similar tasks. In doing this, you will also be able to estimate the cost of integration.
Discuss innovations with employees. It is imperative to ensure that your employees know that you want to implement RPA because it will not be possible without gaining their trust. Their main fear can be that of losing jobs. It can be tackled by clear-cut and up-front discussions with workers to explain the need for automation, its benefits, and how it will better the lives of the employees and patients.
Measure performance. Monitoring the performance of your RPA solution is vital to determining its success. One of the main ways to determine the RPA effectiveness is by measuring the amount of work to be redone after human error against work to be redone after RPA implementation. Control activities also include gathering feedback from employees. Do bots really save them time and make their lives better? If not, either the RPA needs redesigning or people—retraining.

