The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is changing how travel platforms access real-time data. Instead of building many custom integrations, systems can connect to MCP servers that act as a standard interface to existing flight, hotel, rail, and mobility systems. Being the consistent interaction layer, MCP formalizes the connection and tooling model for AI agents, while the underlying data formats and structures continue to be defined and managed by each provider.
For companies building AI agents and similar systems, MCP aims to reduce the effort needed to add new data sources over time. It offers a shared way to discover, link to, and use external tools, with the expectation that this can simplify experimentation and expansion as more MCP servers become available. While still early, the goal is to make AI integrations more reusable and less tightly coupled to individual APIs.
This article explains the current state of MCP use in travel and gives a clear breakdown of the main MCP server types available today.
MCP servers and the problems they solve
Before we look into the benefits of MCP servers, let’s first understand the protocol itself. MCP is a standard that specifies a consistent way for large language models (LLMs) to connect to external systems. It defines how a model can request data, call tools, read resources, or perform actions, reducing the need for AI-side integrations for each service.
MCP creates a common interface between LLM-powered applications and the systems they interact with, making it easier to plug in new capabilities or data sources as needed.
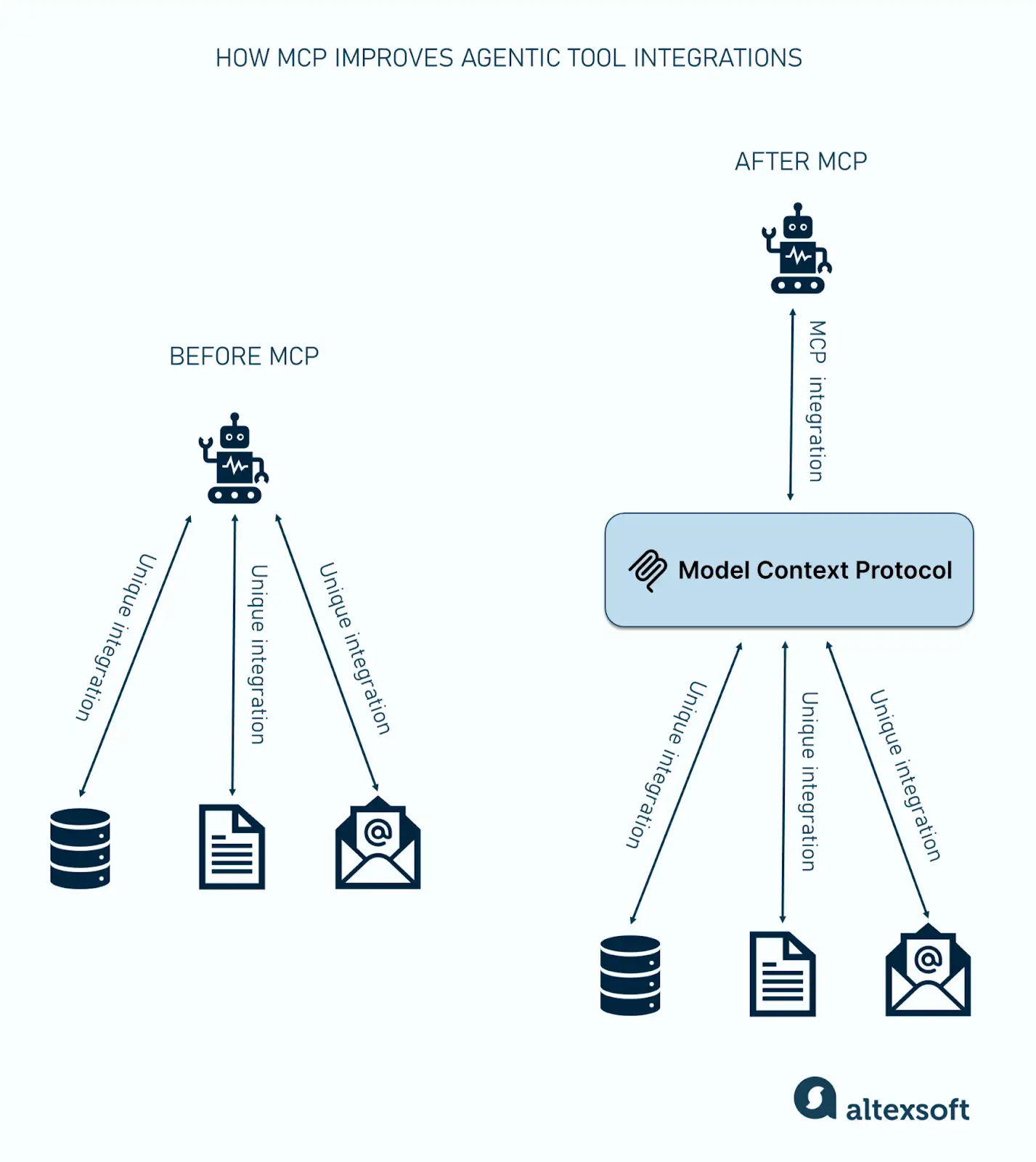
The protocol is just one aspect of the equation. You also need the servers themselves. They are created by companies that want to expose their data or functionality in a format that AI-powered systems can use. They do this by wrapping their existing APIs, business logic, data pipelines, or internal services into the protocol’s structure.
For example, an airline could provide an MCP server that lets AI agents search flights or check availability through one consistent interface.
In the travel industry, where data and services are spread across many systems, vendors, and formats, each new integration can be slow and costly to build. MCP servers help reduce this friction by providing a standard connection layer for exposing existing data and functionality to AI agents, making it easier to operate across a highly fragmented travel ecosystem.
Read our dedicated article for a detailed overview of the Model Context Protocol and its servers.


The current state of MCP adoption in travel
The first thing to understand about MCP adoption in travel is that the protocol itself is still very new. MCP was introduced in November 2024, so the ecosystem is only beginning to take shape. Because of this, adoption across the travel industry is still at an early stage. Most companies are exploring the technology, running pilots, or experimenting internally rather than deploying MCP widely across production systems.
At the moment, there are relatively few MCP servers officially released by travel companies. Instead, a growing number of open-source contributors and independent developers wrap existing travel APIs—such as flight search, hotel content, reviews, or transport data—into MCP-compatible interfaces so AI agents can interact with them. This has created a growing layer of third-party MCP servers built on top of travel services and data sources, even when the original provider has not released an official MCP implementation.


At the same time, a small but important shift is starting to happen: many travel and hospitality companies are now creating official MCP servers, with industry leaders like Kiwi.com and Sabre, launching theirs in 2025. These companies are not waiting for the ecosystem to mature fully. Instead, they are treating MCP as a strategic investment and a way to prepare their platforms for AI-native interactions. There is clearly a strong and growing interest in testing agent-based experiences and understanding how conversational AI will change travel tech.
Now, let’s explore the different types of MCP servers that are currently available across various sectors in the travel industry.
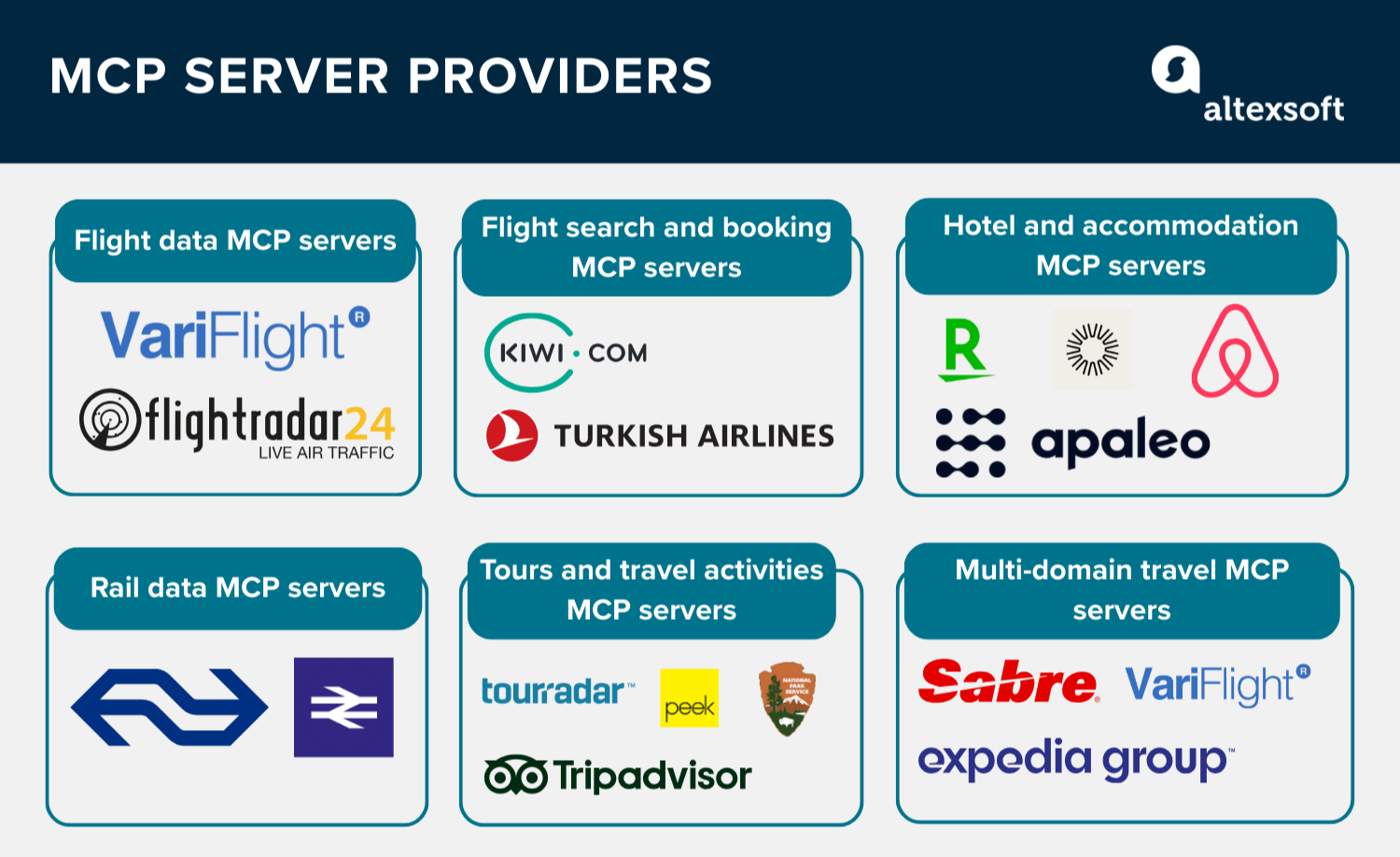
Flight data MCP servers
Depending on the capabilities of the underlying API, these servers can expose data such as flight schedules, live status updates, delays, cancellations, aircraft details, airport-level signals, and weather-related disruptions. Some also provide historical performance data, which AI agents can use to judge how reliable a route or airline might be.
VariFlight Aviation MCP server (official)
VariFlight is a Chinese aviation data technology company that specializes in real-time and historical flight information, airline schedules, and aviation analytics. Its aviation MCP Server gives travel platforms access to real-time aviation data that enables AI agents to query live flight status.
- search flights between airports;
- discover connecting flight options within 48 hours;
- check the in-flight experience, including meals and cabin facilities;
- track aircraft positions via tail numbers; and
- retrieve future weather conditions at destination airports.
The VariFlight MCP server is compatible with LLM-based platforms like Claude and Cursor. It primarily focuses on global flight coverage. However, certain features—like detailed itinerary searches with fare information—are currently restricted to routes within mainland China.
Flightradar24 API MCP server (official)
Flightradar24 is a Swedish flight tracking service and platform that shows real-time aircraft positions, flight numbers, aircraft types, and historical tracks on interactive maps. It gets data from a global network of ADS-B receivers—devices that pick up signals from aircraft—and satellite sources, making it one of the largest flight tracking networks in the world.
The Flightradar24 MCP Server gives agents read-only access to both live and historical flight positions, historical flight events, specific flight tracks, and aggregated flight summaries. It also provides static reference information such as airline and airport details, allowing AI agents to combine operational context with background knowledge.
To use the server, you need Node.js and an active FR24 API subscription.API request/response limits and the depth of available data depend on the pricing plan you choose.
Flight search, booking, and management MCP servers
Flight search, booking, and management MCP servers handle the commercial side of air travel. They let AI agents access available flight options and ancillaries (such as baggage or seat selection), create and modify reservations. The exact capabilities will depend on what the underlying airline or flight aggregator API exposes.
Kiwi.com MCP server (official)
Kiwi.com is a travel technology company that operates an online flight search and booking platform. It offers a Flight Search MCP Server that you can use to build an AI chatbot to let end users plan their trips using natural language queries. The server lets you access round-trip and one-way flights based on:
- origin and destination (city or airport),
- travel dates (with flexible ranges of plus or minus three days),
- passenger number and types, and
- cabin class preferences.
Each response includes a booking link directly to the chosen flight. The server can be installed with your preferred MCP client, including Cursor, Claude, ChatGPT, VS Code, Cline, or Goose.
Turkish Airlines MCP Server (official)
Turkish Airlines is the national flag carrier of Turkey and is one of the few carriers building its own MCP Server that exposes several core airline services for use by AI assistants. This MCP Server’s capabilities include:
- searching flights by route, date, and passenger details, and checking real-time flight status by number or route;
- retrieving booking details, check-in information, and baggage allowances using a PNR and surname;
- generating booking links for selected flight options so users can move quickly from search to purchase;
- providing destination guides, current airline promotions, and curated travel information; and
- accessing information on loyalty program members, such as profile details, flight history, miles balance, and expiring miles.
While the Turkish Airlines MCP server is live and available for use via Claude.ai, Claude Desktop, and VS Code Copilot, it is still under active development. Some features may be refined over time, and new tools or improvements are expected as the platform evolves.
Learn more about Sabre API integration in our dedicated article.
Hotel and accommodation MCP servers
This category of MCP servers connects AI agents to hotel and accommodation data sources that expose descriptions, amenities, location details, prices, availability, and booking policies. Many implementations also support creating, modifying, or canceling reservations, depending on the underlying distribution source.
Rakuten Travel MCP server (unofficial)
Rakuten Travel is one of Japan’s largest online travel agencies (OTAs), and it offers hotel and accommodation bookings. Its travel MCP Server connects AI agents to the Rakuten Travel API, which allows for hotel search and availability checking. Agents can search by dates, room and guest count, and filter results by price range, hotel type, and availability.
To start building a chatbot, you must get a Rakuten Travel API application ID and install Deno runtime—an open-source JavaScript and TypeScript environment for the modern web.
Read about how AltexSoft helped Rakuten Travel optimize revenue with AI predictions.
Kismet Travel MCP Server (official)
Kismet is a software platform that helps hotels become easier to find and book through AI-powered search and assistant tools. It focuses on making hotel information available in conversational AI.
The Kismet MCP server lets tools like Claude, ChatGPT, and other MCP-compatible clients access Kismet’s hotel data. It enables AI agents to search for hotels, access real-time room rates and availability data, and generate booking links that users can follow to complete a reservation.
Apaleo MCP server (official)
Apaleo is the first property management platform in the hospitality sector to launch an MCP server—currently in alpha. The server transforms Apaleo’s 237 core API endpoints into MCP-compatible tools, giving AI agents access to capabilities like checking availability, modifying bookings, creating payment links, building guest profiles, and managing inventory. This makes integration fast and straightforward for AI agents or other AI-powered applications in hotel operations.
Airbnb MCP server (unofficial)
Airbnb is a global hospitality marketplace that allows people to list, discover, and book accommodations around the world. Its Airbnb MCP server allows AI agents to search for Airbnb accommodations and retrieve detailed information about individual properties. It’s designed to work without an API key and returns structured JSON data.
This MCP server’s capabilities include
- searching Airbnb listings based on location, dates, number of guests, pets, and price range.
- Retrieving detailed information for a specific listing, including descriptions, host details, amenities, and pricing.
- Respecting Airbnb’s robots.txt rules while scraping data, or optionally ignoring them with a configuration flag.
- Flattening and organizing data to reduce context load for AI agents.
The server is compatible with Claude Desktop and other MCP clients. It can also be used locally for development purposes.
Rail data MCP servers
Rail MCP servers provide information related to train travel. This includes schedules, routes, delays, fares, ticket booking, etc. Most rail systems are national or regional, so these servers often focus on specific countries or networks.
National rail MCP (unofficial)
National Rail is the shared brand used by passenger rail operators in Great Britain. While individual train companies run the services, National Rail provides unified access to schedules and service information across the UK rail network.
The National Rail MCP server is designed to let AI systems work with UK train timetable data in a structured way. It connects to the Realtime Trains API and focuses specifically on rail schedule information rather than broader services.
Through this server, AI agents can look up live departures and arrivals, as well as planned train schedules for specific dates. This makes it useful for travel planning and real-time rail updates within AI-powered assistants or applications.
Dutch Railways (NS) travel information server (unofficial)
Dutch Railways, known as NS, is the main passenger rail operator in the Netherlands. It runs national and regional train services and provides official data on schedules, delays, routes, stations, and ticket pricing.
The NS travel MCP server connects AI tools to real-time travel data from the Dutch Railways (NS) using the official NS API. It makes it possible to work with up-to-date train schedules, delays, route planning, ticket prices, and station details for travel within the Netherlands.
The server supports journey planning with live updates, provides departure and arrival information, and includes detailed station data such as facilities and accessibility. It also returns ticket pricing across different travel classes and supports queries in both Dutch and English, making it suitable for travel planning and transport-focused AI workflows.
Tours and travel activities MCP servers
Tours and activities MCP servers cover things to do at a destination. This includes attractions, guided tours, events, and local experiences.
These servers provide information about availability, time slots, pricing, and booking rules. Capacity and cancellation policies are often important parts of the context they provide.
TourRadar MCP server (official)
TourRadar is an online travel marketplace that focuses on multi-day tours. It brings together tours from thousands of operators worldwide, covering guided adventures, cultural trips, river cruises, and expedition-style travel.
TourRadar’s MCP server has introduced an MCP server that opens up its inventory of multi-day tours for discovery within AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Perplexity. The goal is to support AI-powered trip search and booking, expanding access to tour content beyond traditional travel websites and into conversational interfaces and developer environments.
The MCP server connects 50,000+ tours from 2,500 operators to chatbots, dev tools, and more.
Through the MCP Server, AI agents can:
- search tours using structured filters (destination, dates, travel style);
- explore tour details and itineraries;
- answer questions about destinations and tours;
- download brochures; and
- create bookings directly through AI prompts.
The MCP server is part of TourRadar’s AI-discovery strategy. There’s also a ChatGPT CustomGPT and an Instagram integration that turns travel reels into bookable multi-day tours.
Peek’s trip planning MCP (official)
Peek helps people find and book experiences, tours, workshops, and activities worldwide. It works as both a consumer marketplace, where travelers can browse and book things to do, and a business platform that provides tools for operators to manage bookings, payments, inventory, and marketing.
The Peek MCP server is a free tool designed for better trip planning. It gives AI travel assistants access to real-time data on activities, tours, and experiences worldwide, enhancing their ability to build personalized itineraries.
This MCP server works fully with ChatGPT and Claude. However, there is only partial support for Gemini and Microsoft Copilot.
MCP server for US National Parks (unofficial)
The US National Park Service is a federal agency responsible for managing national parks, monuments, battlefields, seashores, and other protected natural and historic sites across the United States. Its MCP server allows AI assistants to retrieve a list of all national parks in a specific state and fetch information on a specific park, including description, location, and codes. All information is provided in real-time and powered by the official National Park Service API.
TripAdvisor MCP (unofficial)
TripAdvisor helps people plan trips and make informed decisions by collecting user reviews and ratings for hotels, restaurants, attractions, and other travel experiences worldwide. The TripAdvisor MCP server connects AI assistants to TripAdvisor’s Content API. It exposes location data, reviews, photos, and more, making it easier for AI systems to:
- find hotels, restaurants, attractions, or other points of interest on TripAdvisor;
- get in-depth information about specific locations;
- access user reviews and photos for any listed location; and
- search for locations near specific coordinates.
Together, these capabilities allow AI assistants to use TripAdvisor as a rich source of travel context.
Multi-domain travel MCP servers
These servers represent platforms that combine different aspects of travel into one place. They are designed for wide coverage and standardized workflows, allowing agents to search across multiple products, create bundled bookings, and manage reservations through a single system.
Sabre MCP server (official)
Sabre Corporation runs one of the world’s largest global distribution systems (GDS). Originally built for airline reservations, it now covers hotels, car rentals, and other travel services.
The Sabre MCP server enables AI agents to shop, book, and service trips. The solution builds on Sabre IQ, the company’s AI and analytics layer, and Travel Data Cloud, which aggregates more than 50 petabytes of historical and live travel data. This data foundation spans key travel signals across flights, hotels, fares, and operational events, allowing AI-driven systems to support intelligent retailing, servicing, and disruption handling across the travel lifecycle.
The MCP already powers a set of Sabre agentic-ready APIs, which could support different use cases. For example, you can build
- a Call-Centre Proxy Agent to make same-day rebookings, update passenger calendar, and pay using stored card details;
- a Hotel Ops Agent to confirm late arrivals and address special guest requests;
- a Visa & Compliance Agent to complete online applications, pay fees, and attach required documents to bookings; and
- an Expense Filing Agent to collect receipts and submit full reports in line with the company’s travel policies.
Sabre is embedding its new agentic capabilities directly into SabreMosaic, the company’s modular, cloud-native platform. The approach allows airlines, agencies, and developers to introduce agent-driven workflows within an existing production environment.
Expedia MCP server (official)
Expedia Group, one of the world’s largest booking platforms, allows travelers to search and book hotels, flights, car rentals, cruises, and vacation packages. The capabilities of the travel recommendations MCP server it provides include:
- recommending hotels based on destination, dates, property types, amenities, guest ratings, and sorting preferences;
- suggesting flights according to user-specified criteria,
- offering curated activity and tour recommendations at travel destinations; and
- providing car rental options with customizable parameters.
The server supports multiple connection methods (stdio and streamable-http protocols). This means AI tools can interact with the server either through direct data streams or over web-based connections, depending on the deployment needs.
VariFlight Tripmatch MCP Server (official)
The Variflight Tripmatch MCP server makes it easier to access flight and train information. By wrapping the Variflight API into MCP-compatible tools, it allows AI agents to:
- search flights by departure and arrival cities or airports;
- look up flights by number;
- check transfer options between flights and trains; and
- retrieve related pricing and schedule data.
The server also includes advanced features like a flight happiness index, which evaluates flight options based on punctuality, amenities, health protocols, and comfort, and provides future weather forecasts for airports to help with trip planning. Train travel is supported as well, with tools to search for train tickets between cities or locate train stations by keywords.
How to choose the right travel MCP server
Selecting the right Model Context Protocol server is an essential step when building AI-driven travel workflows. MCP servers can execute code on your system, which means you need to be careful and deliberate in choosing which ones to rely on.
Check for an official MCP server
The first step when choosing an MCP server is to see if the company itself has published one. Official servers are usually the safest choice because they come directly from the source and are maintained according to the company’s standards. If an official server exists, stick with it rather than relying on third-party implementations.
Use directories and community signals
Some MCP server directories, like Glama, make it easier to pick a trusted server by including badges or indicators for security and quality. They also let you know if an MCP server is official. These signals can be helpful, but you should also do your own checks to make sure a server is reliable. Look at the activity, how often it's maintained, the number of users and GitHub stars, and any community recommendations.
Community trust also matters. Some MCP servers are frequently recommended in forums and documentation. In some cases, even when a company does not publish an official server, it may still point developers toward a specific community implementation. These kinds of references are strong signals that the server is considered safe and reliable by people who understand the ecosystem.
Inspect the server code
Whenever possible, take a look at the MCP server code. Understanding what it actually does helps ensure it is safe to run in your environment. Check for unusual behaviors, unnecessary permissions, or operations that could put your system at risk. Code review is especially important if you’re using a community-built or unofficial server.
Build your own server
If no suitable MCP server exists, you can build your own. The MCP documentation provides guidance on how to create a working server from scratch. This gives you full control over functionality, security, and integration. It’s more work upfront, but it removes reliance on third-party servers.
Consider managed vs. self-hosted
Decide whether you want a managed server or to host it yourself. Managed servers are easier to set up and maintain, but you may give up some control over access and data handling. Self-hosted servers provide full control, but you are responsible for updates, security, and uptime. Weigh the pros and cons in the context of your workflow and team capabilities.

With a software engineering background, Nefe demystifies technology-specific topics—such as web development, cloud computing, and data science—for readers of all levels.
Want to write an article for our blog? Read our requirements and guidelines to become a contributor.

